Annunciation Cathedral of the Moscow Kremlin
One of the oldest churches in the Moscow Kremlin stands on the edge of Cathedral Square on the edge of Borovitsky Hill. Many centuries...
5
Pregnancy is a difficult time, a kind of test of the body's strength. Approximately 4% of pregnant women after 15-16 weeks experience so-called gestational diabetes mellitus. In medicine, this is the name for diabetes mellitus, which manifests itself in a woman who is completely healthy in this regard during pregnancy.
At normal pregnancy Blood glucose levels should be as follows: fasting - up to 5.1 mmol/l; 1 hour after a glucose load - up to 10.0; after 2 hours - up to 8.5. If the test results exceed the threshold values, another study is carried out a few days later. And only if discovered high sugar in the blood again, diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance, is determined.
Of course, performing a glucose tolerance test (especially a three-hour test) takes a lot of time. Most likely, the employee’s absence from the workplace. That is why in most antenatal clinics in Russia, pregnant women referred for research are asked to issue a one- or two-day sick leave.
Pregnancy is both a pleasant and difficult time when the body is tested for strength. According to experts, approximately 4% of women after 16 weeks face a problem such as gestational diabetes. It is noteworthy that this pathology can manifest itself in an absolutely healthy woman. To diagnose it, modern medicine suggests using the so-called glucose tolerance test during pregnancy.
According to doctors, this problem can be dangerous not only for the woman herself, but also for the child in the womb. In diabetes, glucose enters the fetal bloodstream directly from the mother, rather than insulin itself. As you know, a child’s pancreas begins to form only in the second trimester. She immediately has to work extra hard to be a mother. The load on the child's gland results in the development of hyperinsulinemia. As a result, the baby is born with low sugar levels, and his breathing may be impaired. As for the women themselves who neglect timely treatment during pregnancy, they experience problems with vision and kidney function.
The likelihood of gestational diabetes mellitus increases several times in the presence of the following factors:
The difficulty of diagnosing gestational diabetes mellitus is that it practically does not manifest itself in any way. external signs, but at the same time, the sugar level increases, and its indicators decrease extremely slowly.
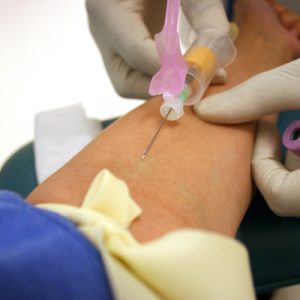
IN in this case The most reliable diagnostic method is a glucose tolerance test. Depending on its length, there are one-, two- and three-hour options.
Today, in almost all antenatal clinics, a glucose tolerance test during pregnancy is prescribed without fail. Experts recommend taking this study at 28 weeks. However, if a woman is at risk, the analysis can be carried out earlier.
In addition, the test is required in the following cases:
If the glucose tolerance test is positive, the woman will be monitored by doctors for the rest of her pregnancy.
First of all, it should be noted that the result of this analysis will be as informative as possible only if the woman takes into account all the recommendations described below.
The test is done only on an empty stomach and in morning hours. The night before, the expectant mother is allowed a light dinner with fermented milk dishes. In the morning you should not smoke, drink alcohol, or take any medications.

In addition, only absolutely healthy women are allowed to take a glucose tolerance test during pregnancy. If a woman is even slightly unwell, it is better to reschedule her visit to the doctor. Otherwise, the results may be somewhat distorted.
Price this study may differ slightly. So, in some medical institutions the final price varies from 750 to 900 rubles. The test result is usually known the next day. The cost of the analysis includes the collection of biomaterial, the glucose itself and the test itself.
How to submit it correctly? In fact, everything is very simple, you must strictly follow all the recommendations below.
The study itself is usually carried out in the morning and always on an empty stomach. Blood is drawn from a finger or from a vein. If on an empty stomach the sugar level does not exceed 6.7 mmol/l, the woman is given a drink diluted in the most ordinary water glucose. For an hour-long test, 50 g of glucose is diluted in 300 ml of liquid, for a two-hour test - 75 g, and for a three-hour test - 100 g. The result is very sweet water. To prevent vomiting, some women add a little citric acid to the solution.

This fairly simple procedure allows you to determine how the body reacts to a “sugar” load. That is why the simplest glucose tolerance test is used during pregnancy. shouldn't be much different. To be more precise, immediately after taking sweet water Glucose levels increase, after an hour they decrease slightly, and after another 60 minutes they reach the initial parameters. If retest shows that glucose levels are still at a sufficient level high level, we can talk about gestational diabetes.
After a few hours (the time depends on which glucose tolerance test was chosen), blood is drawn again. Until this time, the pregnant woman is advised to remain at rest. For example, you can lie down and read a book. Physical exercise(even the most ordinary walk) force the body to expend energy, which directly reduces performance. As a result, the result may be unreliable. In addition, during the analysis itself, you must stop smoking.
If you are asked to take a glucose tolerance test during pregnancy, the normal results should be as follows:
If the results of testing do not correspond to standard indicators, the doctor, as a rule, prescribes a repeat test. It takes place a few days later. Only after two positive results the doctor can make a definitive diagnosis. Based on the first test alone, it is incorrect to talk about the presence of a problem, since the expectant mother could simply violate the basic rules of preparing for the test. As a result, the examination shows a false positive result.

After final confirmation of the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment. During pregnancy, only insulin is allowed. Any kind is strictly contraindicated. Scientists have proven that these medications can negatively affect the development of the fetus inside the womb.
In addition, it is recommended that a woman individually special diet, which implies the exclusion of all easily digestible carbohydrates (chocolate, pastries, cakes, etc.). Only healthy, and most importantly, proper nutrition. It is equally important to constantly monitor the current one. If the indicators are excessively high, it is recommended to call an ambulance.
It is important to note that gestational diabetes most often goes away without a trace immediately after childbirth. This is why doctors today prefer not to prescribe any specific treatment.
In conclusion, we note that the glucose tolerance test is quite informative method, which allows you to confirm the presence of any disorders in carbohydrate metabolism, including in pregnant women. We hope that all the information presented in this article will be truly useful to you.
Procreation is one of the natural laws inherent in every person. At the same time, bearing a child involves increased stress on all vital systems and organs of the expectant mother. It is very important to monitor the development of this condition, carry out the necessary research, correction and timely treatment of emerging pathologies.
A glucose tolerance test is recommended taking into account the fact that a hyperglycemic state is rarely accompanied by complaints and manifestations, but poses a certain danger to the mother and developing child. The optimal time for it is the third trimester of pregnancy, after 24 weeks (no later than 32 weeks).
note
This type of research must also be carried out due to the fact that about 10-15% of pregnant women have a predisposition to latent (hidden) diabetes.
There are certain indications for this:
If these problems are present, it makes sense to conduct a glucose tolerance test from 10 to 16 weeks of pregnancy. Some experts prescribe it even earlier, but there are no objective grounds for this. If the indicators are normal, the study is repeated after 24 weeks.
The analysis is carried out according to the direction of the attending physician. 3 days before it is performed, you should refrain from eating fatty and fried foods, and do not consume smoked meats, cakes, or coffee.
It would be better to limit (but not exclude!) flour and salty foods. That is, the diet should be neutral. Drinking alcohol and smoking are strictly prohibited (unfortunately, some pregnant women allow themselves to do this).
a number of diuretics.
The doctor should be informed if you take any medicinal substance. If possible, you should refrain from using them. If medications are taken without the possibility of a break, then you should be aware of the possible change in the final result as a result of their influence.
Before the analysis itself, in the evening, you should not eat anything, you can only drink water. You should brush your teeth at night, as the toothpaste may contain substances that distort the data.

Before prescribing GTT, it is necessary to take into account possible contraindications:
 The test involves measuring glucose levels three times. The material is venous blood.
carried out on an empty stomach in the morning (at 8-9 o'clock). After blood is taken, the woman is given a diagnostic cocktail to drink, a solution of water (about 200 ml) containing from 75 to 100 g of glucose.
The test involves measuring glucose levels three times. The material is venous blood.
carried out on an empty stomach in the morning (at 8-9 o'clock). After blood is taken, the woman is given a diagnostic cocktail to drink, a solution of water (about 200 ml) containing from 75 to 100 g of glucose.
If a normal value is determined in the first two samples, then 2 hours after taking the “cocktail” you need to take 3 units of blood .
In the case of clearly increased values in the first sample, a sugar load is not required. If the sugar level is increased in 2 servings, then the third measurement is not required.
note
Some pregnant women find it difficult to drink a sweet solution. They may develop nausea, so in this case, you can use a slice of lemon to ease the taste sensation.
Carrying out the test requires relative physical and emotional rest. Except In addition, pregnant women experience weakness during the study. Therefore, they are recommended to stay in a medical institution during the test.
Normally, a woman preparing to become a mother may have higher sugar levels than usual. This is a physiological rise caused by the needs of a growing child.
The norm is:
After 3 hours, the glucose level normally decreases to 7.8 mmol/l.
If the first blood test shows a sugar value above 7 mmol/l, then the presence of type 2 diabetes can be immediately suspected. No further research is required.
If 2 and 3 servings are outside the norm, there are prerequisites for establishing gestational diabetes. Against this background, a repeat study will be required to accurately confirm the pathology and exclude a false result. If it turns out to be positive, then the woman will be recommended to undergo a third study, but after childbirth, to accurately confirm/absence the presence of type 2 diabetes.
note
The glucose tolerance test is absolutely harmless for the expectant mother and her child.
If a diagnosis of “gestational diabetes mellitus” is made, clinical observation and recording are necessary.
An individually selected diet is recommended, for this it is best to seek the help of a nutritionist. A woman definitely needs active walking in the fresh air, moderate exercise and physical exercise - physical therapy.
Those that reduce blood sugar levels are not prescribed. After restoration of normal glucose levels, an annual repeat test is required.
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is a test for glucose tolerance. It helps to identify carbohydrate metabolism disorders during pregnancy and find out how a woman’s body regulates sugar levels. This test can detect gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), an increase in blood sugar levels associated with pregnancy.
GDM can manifest itself even in pregnant women who were not previously at risk, because pregnancy itself is already a fairly significant risk factor for carbohydrate metabolism disorders.
Gestational diabetes usually has no obvious symptoms. That is why it is necessary to do this test on time so as not to miss the disease, because if treatment is not started, GDM can lead to dangerous consequences for both the mother and her child. In the period from 24 to 28 weeks (preferably from 24 to 26) all pregnant women are required to undergo an OGTT with 75 g of glucose.
Stage 1. Up to 24 weeks, the woman donates blood from a vein on an empty stomach and based on the results of this analysis, the first conclusions are made:
Some doctors recommend that if a pregnant woman belongs to a risk group for gestational diabetes mellitus, an OGTT with 75 g of glucose is performed immediately after registration. If the result is negative, repeat the test at 24-28 weeks.
Stage 2. Women who were fine in the early stages are sent for a glucose tolerance test between 24 and 28 weeks.
The OGTT is carried out on a standard diet containing at least 150 g of carbohydrates per day for at least 3 days before the test. Diabetes mellitus cannot be determined when a pregnant woman follows any diet.
It is necessary to carry out OGTT on an empty stomach in the morning, since there should be no food in the stomach for 8-14 hours. Water is allowed. You are prohibited from drinking alcohol at least one day before the test. You must not smoke until the test is completed. You should try not to take any medications that could affect your blood sugar levels (adrenergic blockers, glucocorticoids, multivitamins and iron supplements that contain carbohydrates, etc.).
A glucose tolerance test is not prescribed in the following cases:
The test is carried out in a sitting position. Any physical exercise (even walking) can change the test results. Blood for this study is taken from a vein. The glucometer cannot be used.
Stage 1. Venous blood plasma is sampled. Glucose levels are measured. If the result exceeds the norm (more than 5.1 mmol/l), the test is interrupted and a diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus or manifest diabetes is made. Well, if it is not immediately possible to determine the glucose level, the test continues until the very end.
Stage 2. After drawing blood, a pregnant woman should drink dissolved glucose within five minutes (75 g of dry glucose or 82.5 g of glucose monohydrate is dissolved in 250-300 ml of water). The moment the woman started drinking the glucose solution is the beginning of the test. Glucose solution is a rather sickly sweet drink. Some women experience attacks of nausea and vomiting from it. There is no need to try to drink this solution in one gulp. It is recommended to add a few drops of lemon juice to the glucose solution to add some freshness.
Stage 3. After 1-2 hours after taking glucose, repeated samples of venous blood plasma are taken (it is possible to take a sample only after 2 hours). If blood is drawn after 1 hour and a diagnosis of GDM is made, the test is stopped. In some cases, OGTT is allowed from 75 g of glucose to 32 weeks.
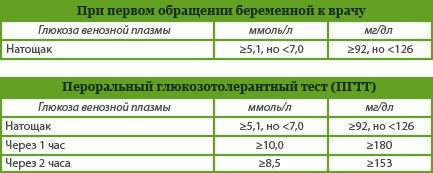
Threshold values of venous blood plasma glucose for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes: (recently, the standards for diagnosing GDM have been tightened, since it has been proven that elevated blood glucose levels have an extremely negative effect on fetal development).
To make a diagnosis of GDM according to the results of a glucose tolerance test, it will be sufficient if at least one of the three indicators is equal to or above the threshold. In total, if the first fasting sample shows a glucose level of more than 5.1, the second stage is canceled, and if the second test after 1 hour shows a glucose level of more than 10.0, the test is stopped and a diagnosis of gestational diabetes is made.
Quite often, clinics use a “breakfast test” - a pregnant woman donates blood (usually from a finger), then eats something sweet and, after some time, donates blood again. Such a test cannot use generally accepted thresholds, since everyone has their own breakfast and the result obtained cannot exclude the presence of GDM.
75 g of anhydrous glucose, diluted in water, is equivalent to breakfast, which consists of a pie with jam. In other words, OGTT is absolutely safe during pregnancy. It is not capable of causing diabetes.
On the contrary, if a woman refuses a glucose tolerance test and gestational diabetes is not identified and the necessary steps are taken to normalize her blood sugar levels, this can lead to serious problems for both the mother and her baby.
Video: Glucose tolerance test.