Herring under a fur coat - a classic recipe
What would New Year be without champagne, tangerines, Olivier, aspic and everyone’s favorite “Herring under a fur coat”. With the last one...
Moxonidine (Physiotens) is an antihypertensive drug used to lower blood pressure in people with hypertension. The main substance of the same name, which is part of the drug, acts on imidazoline receptors of the nervous system, which are located in the ventrolateral part of the medulla oblongata.
One film-coated tablet contains 200 mcg of the active substance moxonidine.
By influencing the system of interneurons, the active substance provokes inhibition of the activity of the vasomotor center. This leads to a decrease in the influence of the sympathetic system on the vascular system and myocardium. The decrease in pressure occurs gradually.
The active ingredient of the drug, moxonidine, has an effect on both blood pressure ( arterial pressure), and on metabolic processes in the body of a patient taking the drug.
For most patients, the active component acts on the body for about twelve hours. It has a complex effect on different systems of internal organs without interfering with the functioning of its systems.
What do Moxonidine tablets help with? The drug is used for arterial hypertension(high blood pressure, hypertension) in the anamnesis.
When taken over a long period of time, the medicine relieves left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy and tissue fibrosis that develops against the background of the underlying disease. In addition, the drug can effectively normalize the capillary blood supply to the myocardium.
In most cases, treatment of high blood pressure with Moxonidine tablets begins with a daily dose of 200 mcg. Taking more than 400 mcg at a time is not recommended.
The maximum daily dose is 600 mcg, which must be divided into 2 doses.
The drug is taken orally, 1 time per day, preferably at morning hours, regardless of food intake. The tablets should be taken with a sufficient amount of liquid.
Features of application
During therapy for hypertension using Monoxidine, patients should be careful. This applies to engaging in hazardous activities and driving a vehicle. After all, the drug affects psychomotor reactions and disrupts concentration, which is confirmed by reviews from many patients.
Treatment with medication requires regular monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate and ECG.
It is advisable to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, since ethanol negatively affects the cardiovascular system and leads to surges in blood pressure.
Most Frequent side effects in patients taking Moxonidine: dry mouth, dizziness, asthenia and drowsiness. These symptoms often improve after the first weeks of therapy.
In addition, the body of a patient taking the medication may react with the following adverse reactions:
Overdose
If therapeutic doses of the drug are exceeded, it may develop severe hypotension, tachycardia, dry mouth, asthenia and drowsiness. Therapy is prescribed depending on the developed symptoms. A specific antidote for imidazolines is idazoxane.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of the drug Moxonidine are: severe bradycardia (less than 50 beats/min), CVS, AV blockade of the second and third degrees, acute and chronic heart failure, lactation period ( breastfeeding), children's and adolescence under 18 years of age, hypersensitivity to moxonidine.
Immediate withdrawal of Moxonidine is prohibited. It is necessary to stop taking moxonidine gradually, over 2 weeks, under the supervision of a specialist.
If the drug is taken simultaneously with beta-blockers, then the drug of this group must first be discontinued, and only after a few days Moxonidine.
Restrictions on use
First degree atrioventricular block, coronary artery disease, ischemic disease heart disease, chronic heart failure, liver failure, renal dysfunction.
There are many drugs based on the active substance - moxonidine. The most famous analogues:
The actions of the drugs are similar. Reviews from doctors about Moxonidine are positive - they confirm its effectiveness in lowering blood pressure, both with rapid relief and with long-term treatment. Both doctors and patients note that Moxonidine effectively lowers blood pressure. In case of severe side effects, the drug can be replaced with a similar drug or a drug from another group.
Important - instructions for use of Moxonidine, price and reviews do not apply to analogues and cannot be used as a guide to the use of drugs of similar composition or action. All therapeutic prescriptions must be made by a doctor. When replacing Moxonidine with an analogue, it is important to consult a specialist; you may need to change the course of therapy, dosage, etc. Do not self-medicate!
LCP-009265/08-211108Trade name of the drug: MOXONIDINE
International generic name(INN): moxonidine.
Compound
active substance: Moxonidine 0.2 mg
Excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, Aerosil A-380, polyvinylpyrrolidone, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropylcellulose (Klucel), castor oil, Tween-80.
Description
Film-coated tablets, round, biconvex, almost white.
ATX code: CO2AC05
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacodynamics
Selective agonist of imidazoline receptors responsible for tonic and reflex control of the sympathetic nervous system(localized in the venterolateral part of the medulla oblongata). Reduces blood pressure (BP). Slightly binds to central alpha2-adrenergic receptors, through interaction with which dry mouth and sedation are mediated.
Reduces tissue resistance to insulin.
Effect on hemodynamics: a decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure with single and long-term use of moxonidia is associated with a decrease in the pressor effect of the sympathetic system on peripheral vessels, a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance, while cardiac output and heart rate (HR) do not change significantly.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption after oral administration is 90%. Food intake does not affect the amount of absorption. Bioavailability - 88%. Communication with blood plasma proteins - 7%. C max in plasma is determined 30-180 minutes after oral administration and is 1-3 pg/ml. Volume of distribution - 1.4-3 l/kg. Passes through the blood-brain barrier. Does not accumulate with prolonged use. The half-life is 2-3 hours. 90% is excreted by the kidneys (70% unchanged, 20% in the form of metabolites). No significant differences in pharmacokinetics were found in young and elderly patients.
Indications for use
Arterial hypertension.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, sick sinus syndrome, sinoatrial and atrioventricular block II and III degrees, severe bradycardia (heart rate less than 50 beats/min.), chronic heart failure class III and IV (NYHA classification), angioedema history, unstable angina, severe liver failure, chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min., creatinine more than 160 µmol/l), age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established), pregnancy and lactation, simultaneous administration with tricyclic antidepressants.
Carefully: Parkinson's disease (severe), epilepsy, glaucoma, depression, intermittent claudication, Raynaud's disease, first degree atrioventricular block, chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance more than 30, but less than 60 ml/min.), cerebrovascular diseases, after a heart attack myocardium, chronic heart failure class I and II, severe liver failure - due to lack of experience in use, hemodialysis.
Method of administration and dosage
Inside, regardless of food intake, with a sufficient amount of liquid. In most cases, the initial dose of moxonidine is 0.2 mg per day, in one dose, preferably in the morning. If the therapeutic effect is insufficient, the dose can be increased after 3 weeks of therapy to 0.4 mg per day in 2 doses or once. The maximum daily dose, which should be divided into 2 doses (morning and evening), is 0.6 mg. The maximum single dose is 0.4 mg.
In elderly patients with normal renal function, dosage recommendations are the same as for adult patients.
In patients with renal failure (cretinin clearance 30-60 ml/min.) and patients undergoing hemodialysis, single dose should not exceed 0.2 mg, maximum daily dose 0.4 mg.
Side effect
Especially at the beginning of therapy, the most common adverse reactions were: dry mouth, headache, dizziness, asthenia, peripheral edema, allergic reactions, nausea, constipation, drowsiness. The intensity of their manifestation and frequency decrease with repeated use. Cases of anorexia, parotid pain, urinary retention or incontinence, dry eyes, orthostatic hypotension, Raynaud's syndrome, endocrine disorders, cholelithiasis.
Overdose
Symptoms: headache, sedation, drowsiness, excessive decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, general weakness, bradycardia, dry mouth, vomiting, fatigue, stomach pain. A short-term increase in blood pressure, tachycardia, and hyperglycemia are also potentially possible.
Treatment: symptomatic. Gastric lavage (immediately after administration), administration of activated charcoal and laxatives, symptomatic therapy. If blood pressure decreases, it is recommended to restore circulating blood volume by administering fluids. Bradycardia can be relieved with atropine. Alpha-adrenergic antagonists may reduce or eliminate transient hypertension following moxonidine overdose. Idazoxan (an imidazoline antagonist) is administered as a specific antidote.
Interaction with other drugs
Moxonidine can be prescribed with thiazide diuretics and slow calcium channel blockers. At joint use moxonidine with these and others antihypertensive drugs there is a mutual enhancement of the action of moxonidine.
When prescribing moxonidine with hydrochlorothiazide, glibenclamide (glyburide) or digoxin, there is no pharmacokinetic interaction.
Tricyclic antidepressants may reduce the effectiveness of centrally acting antihypertensive agents.
Beta-blockers increase bradycardia and the severity of the negative ino- and dromotropic effects of moxonidine.
Moxinidine moderately enhances decreased cognitive performance in patients taking lorazepam.
Prescribing moxonidine together with benzodiazepines may be accompanied by increased sedative effect the latter.
When moxonidine is prescribed together with moclobemide, there is no pharmacodynamic interaction.
special instructions
If it is necessary to cancel simultaneously taken beta-blockers and moxonidine, first cancel the beta-blockers and, only after a few days, moxonidine. It is not recommended to prescribe tricyclic antidepressants simultaneously with moxonidine. During treatment, alcohol consumption is excluded. During treatment, regular monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate and ECG is necessary.
Moxonidine can be prescribed with thiazide diuretics, ACE inhibitors and slow calcium channel blockers.
Moxonidine should be stopped gradually.
Influence on the ability to drive a car and control machines and mechanisms
There is no data on the adverse effects of moxonidine on the ability to drive a car or operate machinery. There are reports of drowsiness and dizziness during treatment with moxonidine. This should be taken into account when performing the above steps (especially at the beginning of treatment).
Release form.
Film-coated tablets, 0.2 mg. 10 or 14 tablets in a blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film and aluminum foil. 1, 2, 3 or 4 blister packs of 10 tablets or 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 7 blister packs of 14 tablets along with instructions for use in a cardboard pack.
Best before date
3 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
According to the recipe.
Manufacturer/organization accepting claims:
Federal State unitary enterprise Research and Production Center "Pharmzashchita" of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency (NPC "Pharmzashchita"). 141400, Khimki, Moscow region, Vashutinskoe highway, no. 11.
Moxonidine, analogues of which are prescribed if it is impossible to take the drug due to contraindications or the development of side symptoms, is a medicine that is used for arterial hypertension in adults. Prescribed only by your doctor; self-administration may lead to negative reaction body.
Contents [Show]
Moxonidine tablets are prescribed for arterial hypertension. The drug is taken once a day, preferably in the morning. There is no connection to eating. The tablets do not need to be chewed; they are swallowed whole with plenty of water. The dosage of the drug is individual, depending on the age of the patient and the severity of the clinical picture. In case of complex forms of hypertension, the doctor prescribes the maximum dosage.
Contraindications to taking Moxonidine:
It is prohibited to use by patients under the age of majority. If it is necessary to treat arterial hypertension in children, milder analogues are prescribed. The tablets are not intended for people over 75 years of age due to the high risk of developing possible complications and the presence of diseases inherent in this age group, which are a contraindication for use. Women are prohibited from taking this medication during breastfeeding.
Moxonidine, the instructions for use of which should be carefully studied before use, is a drug with a high content of active substance, therefore the risk of developing side symptoms cannot be excluded in cases where the patient takes increased dosage or cannot use this medicine due to contraindications.
If the dosage prescribed by the doctor is exceeded, side symptoms may develop:
If a person with kidney failure takes Moxinidine, there is a possibility of developing hepatitis. In men, prolonged use of increased doses of the drug can provoke impotence.
If the medicine cannot be taken due to contraindications or the occurrence of side symptoms, analogues of the drug are prescribed:
When taking the drug Moxonidine, you must be careful while driving a car and when working with complex mechanisms. The active components of the drug can negatively affect the functioning of the central nervous system and depress attention and concentration.
One of the analogues of this medicine- Moxonidine Canon, in which the concentration of the main substance is slightly lower than in the main drug, which makes it milder in relation to the effect on the patient’s body. The medication should not be taken if you have the following diseases and pathological processes in the body:
Moxonidine Canon is contraindicated for people undergoing hemodialysis, women during breastfeeding. The drug is not prescribed if it is necessary to take medications of the tricyclic group. In the presence of individual allergic reactions to individual components medicine the medication must be replaced with analogues.
Moxonidine Canon should be used with extreme caution by people who have pathologies circulatory system, especially the coronary arteries. Special instructions for the use of the drug apply to patients with diagnoses such as depression, epilepsy, glaucoma, and mild stages of liver failure. These diseases are not strictly contraindicated to the use of Moxonidine Canon, but in patients with a history of these pathologies, the risk of developing side symptoms increases, and therefore the dosage is prescribed on an individual basis. If any complications are detected, you must immediately stop taking the drug and inform your doctor.
Unlike the main drug, Moxonidine Canon has a lower percentage of similarity to the alpha 2 adrenergic receptor substance, and therefore the risk of developing side symptoms is lower. This concerns the occurrence of dryness in oral cavity, the sedative effect is significantly smoothed out.
The medicine is prescribed for arterial hypertension in cases where the patient cannot take the main medication Moxonidine due to individual intolerance to individual components of the drug. C3 can be used during pregnancy, but only after consultation with the attending physician and only in cases where the use of the drug will bring a positive effect and it outweighs the risk of adverse symptoms.
Contraindications for use are the same as for other analogues. But during lactation, C3 is prohibited, since its active components penetrate into the milk and through it into the child’s body, which can negatively affect his general condition.
Medicine prescribed by a doctor should only be taken when specified dosage If it is exceeded, side symptoms may develop. IN medical practice There are known cases of C3 overdose. Its symptoms:
If these signs are detected, you should immediately contact medical assistance, rinse the stomach. When the decrease in blood pressure reaches critical levels, therapeutic therapy is prescribed, in which the patient is administered atropine.
Moxonidine analog Physiotens has a similar composition and spectrum of action, but there is much less active substance in it, which allows it to be used by people who cannot take Moxonidine due to hypersensitivity or high risks of developing negative symptoms.
Indication for use: arterial hypertension. Unlike Moxonidine, its analogue has fewer contraindications. Physiotens can be taken by people undergoing hemodialysis, but in this case the dosage is calculated individually and, as a rule, is minimal at the beginning treatment course. In the absence of side symptoms and if the body has accepted the medication well, the dosage can be slightly increased.
Physiotens can be taken by pregnant women, but only with the permission of a doctor and in cases where other medications do not provide positive dynamics. If there is a need to take Physiotens during breastfeeding, it is recommended to temporarily transfer the child to infant formula until the course of treatment is completed, or change Physiotens to an analogue with a softer composition and a gentler effect.
Side effects that may be caused include: excessive consumption the drug, an individual allergic reaction to its components, or if the patient takes the drug despite the presence of contraindications, headache and vomiting, clouding of consciousness, weakness in the arms and legs, and a rapid decrease in blood pressure are observed.
For diseases such as Parkinson's, glaucoma, depression, Raynaud's, it is necessary to take the drug Physiotens with extreme caution and under the supervision of a doctor. If your condition suddenly worsens, you should stop taking the medication and consult a specialist.
Moxonidine Sandoz is a medication for the treatment of arterial hypertension, which is an analogue of Moxonidine, but with a milder effect on the body. The active components are quickly absorbed by the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. It is better for children not to take this medication, since clinical trials have not been conducted on this group of patients, and therefore the benefits or harms of taking Moxonidine Sandoz in a group of patients under 18 years of age have not been proven.
Contraindications to the use of Sandoz are similar to other analogues, only heart failure, ischemia, malignant arrhythmia, as well as individual allergic reactions to individual components of the drug are added.
The tablets can be taken regardless of meals. At the beginning of the treatment course, the dosage should be minimal. This is done to test the body to see how well it tolerates this remedy. If no side effects are identified several weeks after taking the drug, the dosage can be increased, but this is decided only by the attending physician.
Special instructions for the use of the drug apply to people with renal and liver failure. In such cases, the dosage is calculated individually, and the medicine is taken only under the supervision of a doctor. If found side effects- nausea, dizziness - you should immediately stop taking the medicine and consult a doctor so that he can replace the medicine with an analogue.
At the beginning of the treatment course, the patient may experience dry mouth. The intensity of this symptom increases or decreases throughout treatment. This symptom does not require discontinuation of the drug, but if it becomes pronounced, it is necessary to adjust the dosage.
Moxonidine should not be taken by people with individual allergic reactions on individual components of the drug, in which the content of the main substance is very high. In such cases, its analogs are prescribed, for example, Moxonidine LF.
The dosage of the medicine is selected individually. It depends on blood pressure and general condition patient. Among the possible side effects, dryness in the mouth is most often observed. This symptom is a normal reaction of the body to the action of the active components of the drug, but if it does not go away within long period time or intensifies, you must contact your doctor to adjust the dosage.
Taking the drug does not depend on diet, but it is better to take Moxonidine LF in the morning. For what? To ensure that the active substances of the drug are better absorbed in gastrointestinal tract and the person felt fine throughout the day.
The drug should not be taken during breastfeeding, by persons under 18 and over 75 years of age. During pregnancy - only if there is no positive dynamics from taking other medications or it is impossible to take them due to contraindications.
This drug, intended for the treatment of arterial hypertension, affects the central type links, which have a direct effect on the process of increasing blood pressure. The active substances of drugs are agonists, which, penetrating the central nervous system, inhibit processes affecting the circulatory system, leading to a rapid increase in blood pressure.
Moxonidine is good effective drug, like its analogues, moreover, they are also relatively safe, the risk of complications with the correct dosage is minimal.
Treatment of arterial hypertension often requires the use of non-standard approaches - not the usual drugs, such as Bisoprolol or Enalapril, are prescribed, but second-line drugs, which are an alternative option.
Typical representatives of the pharmacological group are Moxonidine, Russian analogues and foreign drugs which can only be recommended by the attending physician.
According to the modern classification of antihypertensive drugs, all drugs whose action is aimed at lowering blood pressure are divided into first- and second-line representatives.

Tablets Moxonidine 0.2 mg
Treatment of arterial hypertension always begins with the prescription of a first-line drug (these include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers, diuretics, sartans and slow calcium channel blockers), however, if it is ineffective, as well as in the absence of positive result from the use of a combination of drugs in this category, a second-line agent is prescribed.
A typical representative of the pharmacological group under consideration is Moxonidine, a drug that affects the brain, due to which it is realized clinical effect.
It should be noted high efficiency of this drug, which is combined with the presence large quantity unwanted side effects (it was this feature that was the reason that the entire pharmacological group is considered reserve drugs).
Taking it quite sharply reduces blood pressure levels - on average, blood pressure values drop by 30-40 divisions within half an hour, so after taking the drug, doctors recommend not getting out of bed for about 40-60 minutes, no less, in order to avoid dizziness and fainting.
In terms of its action, this drug has much in common with clonidine, but does not have such a strong hypnotic effect.
The active ingredient is moxonidine, and all other names that can be heard are nothing more than trade names Moxonidine of the same drug (eg,
Moxarel
The mechanism of action of the drug Moxonidine is as follows:

Moxonidine and its analogs are contraindicated in the following cases:

 The drug Moxonidine is available in the form of tablets of 0.200 mg.
The drug Moxonidine is available in the form of tablets of 0.200 mg.
The initial dosage of the drug is 0.200 mg per day, it is recommended to prescribe therapy with a single dose.
No addiction to this drug was observed, however, in the event of progression of arterial hypertension (and it still occurs sooner or later), it is recommended to increase the daily dose of the drug rather than adding drugs from another pharmacological group. This is the main difference in the principles of treating patients with first- and second-line drugs.
Please note that Moxonidine can be taken three times, but the daily dose should in no case exceed 0.600 mg. If necessary, the tablets can be divided in half; this will not affect the effectiveness of treatment in any way. When combining Moxonidine with any drug from the pharmacological group of beta-blockers, the principle of gradually replacing one drug with another should be observed.

Bisoprolol tablets 2.5 mg
For example, if treatment began with 0.200 mg Moxonidine and 5 mg Bisoprolol, then after a week it will be necessary to switch to 0.100 mg Moxonidine and 10 mg Bisoprolol, and after another week use only Bisoprolol alone (if 10 mg is enough to achieve a clinical effect, then not should increase the dose).
To be fair, it should be noted that such a need arises extremely rarely; usually, if a clinical effect is achieved by using Moxonidine, then it is not replaced with anything.
 Often, patients take ACE inhibitors not so much to lower blood pressure, but to protect the kidneys from the harmful effects of vascular hypertension, so taking them together with centrally acting drugs is quite justified.
Often, patients take ACE inhibitors not so much to lower blood pressure, but to protect the kidneys from the harmful effects of vascular hypertension, so taking them together with centrally acting drugs is quite justified.
If the drug Moxonidine should be taken in the morning, then ACE inhibitor should be consumed within 6-8 hours. It is this period of time that best contributes to the harmonious potentiation of the effects of drugs.
But it is much more difficult to combine Moxonidine with inhibitors of slow calcium channels (this need arises if the former are used as an antiarrhythmic). As a rule, Verapamil or Diltiazem is used. Here it will be necessary to titrate the dose of each drug - this is the task only of the attending cardiologist.
When canceling Moxonidine, you should also be guided by the same rule - only gradual withdrawal will avoid the occurrence of many unwanted side effects, so you should stick to the same scheme - 0.400 mg - 0.200 mg - 0.100 mg and only then cancel.
We are not talking about analogues, but about Moxonidine, produced by various manufacturers operating in the Russian Federation:

 In fact, if drugs for lowering blood pressure that belong to the first line can be replaced and varied, selecting the most successful combination, then with centrally acting antihypertensive drugs everything is somewhat different - replacing one with another can only be done in as a last resort, and even then, such a scenario would be extremely undesirable.
In fact, if drugs for lowering blood pressure that belong to the first line can be replaced and varied, selecting the most successful combination, then with centrally acting antihypertensive drugs everything is somewhat different - replacing one with another can only be done in as a last resort, and even then, such a scenario would be extremely undesirable.
The main reason is that a certain sensitivity is developed to all centrally acting drugs, as a result of which the withdrawal syndrome will be extremely pronounced.
In this case, we have to talk not about drug analogues in the literal sense of the term, but about generics:
So, if there is no domestic drug on pharmacy shelves, there is plenty to choose from.
To be fair, it should be noted that domestically produced analogues of Moxonidine are in no way inferior in quality to foreign ones - moreover, they have all received GMP certificates, which once again confirms the compliance of products of Russian companies with international quality standards.
Description and instructions for use of the drug Moxonidine in the video:
You may come across the statement that Clonidine is an analogue of Moxonidine, and one drug, if necessary, can be easily replaced with another. But in fact, this is absolutely not the case - they have no similarities, except that both drugs belong to the same pharmacological group. Even the recommended dosages differ, not to mention the contraindications and side effects.
Be careful, the drug is prescribed to women during pregnancy, when there is no negative impact, affecting the condition of the mother and her child. Behind medical product buyers pay 270-780 rubles.

In addition to the original medicine, cheap analogues of the drug are produced.
Ingredient composition similar to Russian production, contains the main active substance.

| Name | Price in rubles | About the drug |
| Moxarel | from 13-350 | Inexpensive and effective drug. After using the medication it decreases systolic pressure, the composition of the drug interferes with the action of the vasomotor center. A product from a domestic manufacturer has an active effect known disease- arterial hypertension |
| Moxonidine | from 115-220 | Inexpensive and effective medicine. Similar imported drugs are used to treat high blood pressure. Children and adolescents under 16 years of age should not take the medicine |
| Moxonidine Canon | from 145-240 | Inexpensive and effective drug. A similar medicine containing a similar active drug. |
The group of pharmacological medicines includes similar medicines produced in Ukraine. The products are inexpensive compared to the originals.

The list contains synonyms of the original product, they are not considered substitutes similar to the original ingredient.
Similar medicines contain similar indications for use as the original product.
The product is sold at an average price of 15-120 rubles. By type, clonidine is produced in two forms:
Clonidine hydrochloride is one of the main active substances. Modern medications are antihypertensive, arterial hypertension is the area of application. In addition to these diseases, the product treats high blood pressure.
The cheapest analogue is purchased at a price of 45-55 rubles. The tablets have a pronounced hypotensive effect.
The drug is intended to increase renal blood circulation, it has a strong antiarrhythmic effect.
Thanks to the effectiveness of the drug Ruanatine, you can calm frayed nerves. Cheap Ukrainian-made products are used to treat mild and moderate arterial hypertension.
The medicine is available in pharmacy kiosks at average cost from 40-65 rubles. The drug is intended to lower high blood pressure and is purchased at a low cost.
The active ingredient of the drug is maleate. It has the following indications for use: treats arterial hypertension, which requires complex therapy.
Inexpensive Belarusian generics containing the active element moxonidine are suitable as a replacement for a cheap product.

Medicines made in Belarus, which are similar in composition and action to tablets, are found in small quantities. The table below consists of one title.
Below is a list of imported medications that can be replaced inexpensive means antihypertensive action.

The medicine is sold at an average price of 180-600 rubles. The main ingredient is the constituent substance of the medicine. Arterial hypertension is treated with medication.
Tablets made in Germany. Products are sold at an average price of 185-59 rubles.
The ingredient is intended for the treatment of acute diseases:
Has no negative effect on cardiac output, and also does not affect the normal heart rate.
Apply medicinal product to eliminate a disease such as arterial hypertension, with varying degrees of complexity.
The analogue is sold in pharmacy kiosks, with average prices ranging from 300-380 rubles. The product belongs to the group of antiadrenergic drugs, the synonyms of the analogue have a central effect. Prescribed to patients with arterial hypertension.
Symptoms such as dizziness, drowsiness, as well as dry mouth, are considered common adverse events.
The severity of side effects decreases sharply if you are treated with tablets for a long time. According to a doctor's prescription, patients buy products at a pharmacy kiosk.
© 2017 Women's magazine | Womans7 · Copying site materials without permission is prohibited
One tablet contains 200 mcg of active ingredient moxonidine.
Microcrystalline cellulose, Klucel, Aerosil grade A-380, castor oil, polyvinylpyrrolidone, Tween-80, magnesium stearate.
The drug is produced in film-coated tablets, in cellular packaging of 14 pieces, in a cardboard pack there can be 14, 28 pieces - 1 or 2 blisters.
Antihypertensive effect.
Active substance moxonidine is selective agonist imidazoline receptors and is responsible for tonic and reflex control of the sympathetic nervous system, localized in the medulla oblongata in the venterolateral section. The drug is able to reduce systolic and diastolic HELL with a one-time dose and long-term therapy due to the reduction pressor influence sympathetic system on peripheral vascular resistance and peripheral vasculature, without significant changes in cardiac output and heart rate.
Absorption occurs 90% regardless of meals. Bioavailability is 88% and 7% is protein bound blood plasma. The substance can pass through blood-brain barrier, penetrate into milk, long-term use does not lead to accumulation. The maximum concentration in plasma is reached after 0.5-3 hours and is 1-3 picograms per ml, taking into account that the volume of distribution is in the range of 1.4-3 liters per kg. The half-life is several hours. 90% is excreted by the kidneys, with 70% unchanged, the rest in the form metabolites.
The drug is prescribed for arterial hypertension in the anamnesis.
hypersensitivity to the components included in the drug; sick sinus syndrome; violations of the upper atrial and atrioventricular conduction of the 2nd - 3rd degree; pronounced bradycardia when the heart rate is less than 50 beats per 1 minute; severe forms arrhythmias; heart failure; presence in the anamnesis of information about the experience angioedema; glaucoma; pronounced violations normal functioning liver and kidneys; various disorders of peripheral blood circulation, including Parkinson's disease, Raynaud's disease, obliterating atherosclerosis, intermittent claudication syndrome; epilepsy; depression; unstable angina pectoris; intolerance galactose, or shortage lactose, or malabsorption of glucose and galactose; pregnancy or period lactation; age category up to 18 years old.
Moxonidine may cause the following: adverse reactions:
vomit, dyspepsia, dry mouth, diarrheanausea; skin rash , itching; increased fatigue ; asthenic condition; migraine; dizziness(vertigo); various sleep disorders or drowsiness; nervousness; orthostatic hypotension or bradycardia; peripheral edema.
Taken orally, starting with a dose of 200 mcg once a day. The maximum acceptable single dose should be no more than 400 mcg, while the acceptable daily dose should be up to 600 mcg in two doses. Instructions for use of Moxonidine indicate the need to adjust the daily dose on an individual basis based on data on the tolerability of therapy.
Accompanied headaches And dizzy, sedative effect, vomiting, cramps in the stomach, excessive decrease in blood pressure with general weakness and dry mouth. Treatment is prescribed symptomatically in the form of gastric lavage, introductions activated carbon and laxative.
Reducing blood pressure requires restoring blood volume by administering saline solution, bradycardia is stopped Atropine.
Specific antidote Idazoxan- well known imidazoline antagonist.
Combined use of the drug Moxonidine with by the following means and drugs leads to:
With antihypertensive drugs - to additive effect. With tricyclic antidepressants, tranquilizers, ethanol, sedatives and sleeping pills– the effect of Moxonidine may be enhanced. Lorazepam- improvement of weakened cognitive functions. To enhance the sedative effect of derivatives benzodiazepine.
On prescription.
In a dry, dark place, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Up to three years.
Treatment requires regular monitoring HELL, Heart rate And ECG, it is advisable to exclude drinking alcohol, working with machinery and driving a car, as well as other activities that require increased attention or high reaction rates. It is necessary to stop the course gradually.
If cancellation is necessary at the same time β-blocker c and Moxonidine, then β-blockers must initially be discontinued, then after a few days Moxonidine can be discontinued.
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Synonyms of this drug contain the same active substance, while analogues of Moxonidine (or in other words - generics) may only have a similar therapeutic effect, among them the most popular are:
Physiotens; Tenzotran; Moxonitex.
Many people, especially those who are obese, are susceptible to sudden changes in blood pressure. diabetes mellitus, as well as patients who have crossed the 45-year mark. To normalize the condition and relieve the patient of hypertension (or to help quickly lower blood pressure during a hypertensive crisis), doctors prescribe antihypertensive medications. These include Moxonidine. What kind of medicine is this, who is it indicated for, and in what dosage should it be taken?
Trade international name Moxonidine - Moxonidine. It is a selective imidazoline receptor agonist, available in tablet form.
Today there are several forms of Moxonidine on the market from different manufacturers:
The tablets have the same appearance, regardless of the manufacturer of the drug: round, biconvex, white, coated.
The price of the drug depends on the manufacturer, the number of tablets in the package, and the dosage. You can purchase it at the prices presented in the table (Table 1).
Table 1 - Average cost of Moxonidine
| Name, dosage, pcs. | Price, rubles |
|---|---|
| Canon 0.2 No. 14 | From 101 |
| Canon 0.2 No. 28 | From 132 |
| Canon 0.4 No. 14 | From 150 |
| Canon 0.4 No. 28 | From 218 |
| SZ 0.4 No. 14 | From 157 |
| SZ 0.2 No. 28 | From 164 |
| SZ 0.4 No. 28 | From 243 |
| SZ 0.2 No. 60 | From 261 |
| SZ 0.4 No. 60 | From 405 |
| Pharmprotection 0.2 No. 20 | From 146 |
| Vertex 0.2 No. 14 | From 107 |
Moxonidine will contain the active substance moxonidine, registered by the World Health Organization. Excipients include:
Moxonidine is a selective imidazoline receptor subtype 1 agonist that affects the brain and nervous system. The drug works to reduce the activity of the autonomic nervous system and gently lowers blood pressure. In addition, he:

In terms of its effect on the body, moxonidine is comparable to clonidine, but it does not have a powerful sedative effect and does not cause as many side effects during treatment.
Once in the bloodstream, the active substance stimulates imidazoline receptors located in the structure of the brain. When taken internally, the drug is absorbed almost completely (90%). Eating does not affect absorption.
The maximum concentration of the active component in plasma is achieved in 1-3 hours. With long-term use it does not accumulate. Dihydrogenated moxonidine, the main active element, is eliminated naturally within 24 hours.
Moxonidine is a narrow-spectrum drug that is prescribed for high blood pressure (hypertension, hypertension). It is especially suitable for people suffering from obesity and diabetes.
Long-term use helps prevent myocardial hypertrophy and tissue fibrosis, which develops as a concomitant pathology. In addition, the medication is able to normalize the capillary blood supply to the heart muscle.
The medicine lowers systolic and diastolic blood pressure, reducing the activity of the vascular center without affecting the heart rate. It is used for:
Moxonidine is not prescribed for:

The drug is used with caution when:
In medical practice today, two forms of Moxonidine are most often used - LF, North Star and Canon. Let's take a closer look at their differences and reception features.
The tablets are taken regardless of food intake, preferably in the morning (if daily dosage does not require double use). In most cases, the therapeutic constant dose is 0.2 mg at a time (in the morning). The maximum daily intake is 0.4 mg.
Depending on the tolerability of the drug, the daily dose is adjusted on an individual basis. If the therapeutic effect is not enough, then after three weeks of initial therapy, the dose is increased to 0.4-0.6 mg per day, in two approaches.

In case of hypertensive crisis, it is allowed to take 1 tablet three times a day as an emergency aid. You should not take more than 2 tablets at one time. Moxonidine acts quickly: within 15-20 minutes after taking it, blood pressure drops.
For moderate and severe renal failure, as well as for hemodialysis, the initial dose is 0.2 mg, and can be increased to 0.4 mg. For elderly patients with normal operation kidney recommendations for taking the drug are the same as for all other patients.
For emergency treatment of high blood pressure, the tablet is placed under the tongue and dissolved. To avoid overdose and side effects, the dose and duration of the course are calculated by the doctor individually.
One of the types of Moxonidine is Canon, which contains some other additional components (hyprolose, mannitol, magnesium stearate, cellulose), which makes its effect on the body milder.
Canon, unlike the main drug, contains a lower percentage of similarities with selective alpha2-adrenergic receptor stimulants, so the risk of developing unpleasant symptoms is much reduced. This applies to dry mouth and drowsiness.
 This medicine is not used for:
This medicine is not used for:
Canon is not used to treat patients on hemodialysis and women who are breastfeeding. If there is hypersensitivity to the active components, the drug product is replaced with another drug.
Moxonidine Canon should be used with extreme caution in case of pathology of the circulatory system, depression, epilepsy, glaucoma, and mild stages of liver failure.
These conditions are not a direct contraindication to use, but can aggravate the course of the underlying disease and cause side effects. In such cases, the dosage is calculated separately for each patient. If any complications arise, the drug is immediately discontinued.
Antihypertensive medication should not be prescribed to yourself without consulting a specialist, otherwise it can cause serious consequences.
This serious medicine can cause the following side effects (especially at the beginning of therapy):
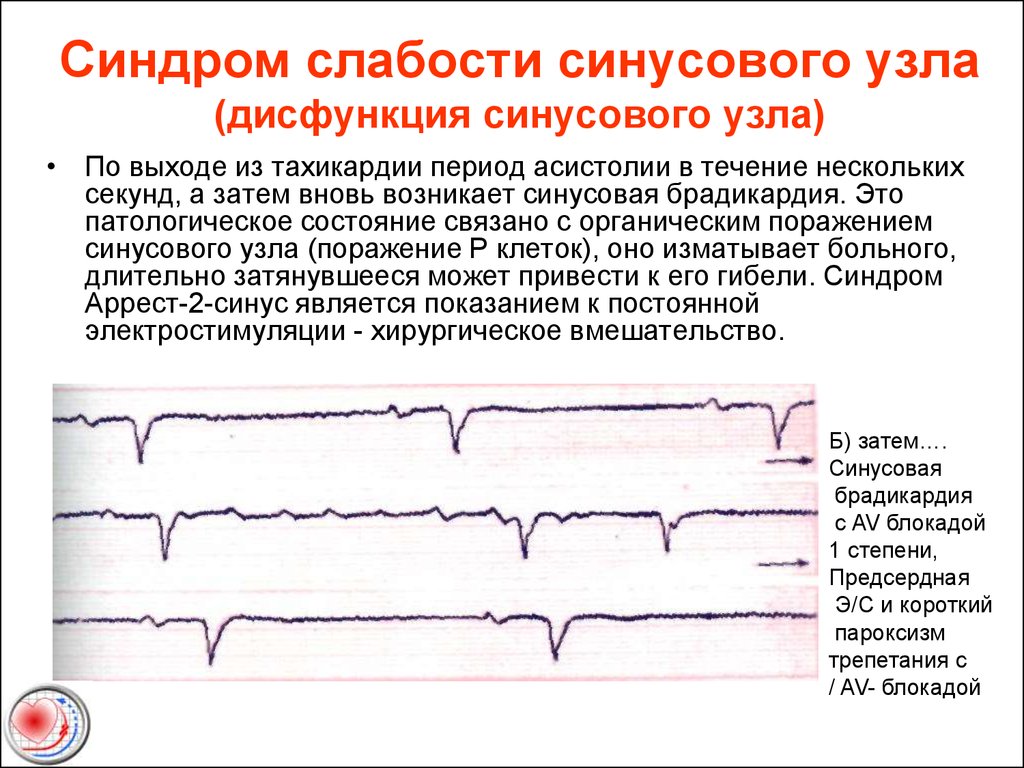
With repeated use, the intensity and severity of unpleasant symptoms decreases. In some cases, patients treated with this drug have experienced:
When carrying a child, Moxonidine is not prescribed, since there is no information on the effect on the intrauterine development of the fetus. The drug can be used by a pregnant woman if the benefit to the mother exceeds possible risks for a child. The active components can penetrate into milk in large enough quantities to harm the baby. Therefore, breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment.

The effectiveness of the drug and its safety when used in children have not been established, so it is not used in pediatrics. It is also prohibited to use this remedy for patients over 75 years of age.
When driving a car and operating machinery that requires increased concentration, you should be as careful as possible: Moxonidine affects the psychomotor reaction.
In case of overdose, the following symptoms may appear:

A short-term increase in blood pressure, tachycardia, and surges in blood sugar levels are also possible.
In cases where the described disorders occur, symptomatic treatment is used. Immediately after taking an excess dose of the drug, it is necessary to rinse the stomach and use laxatives. When pressure decreases, it is recommended to normalize the volume of circulating blood through infusion/administration of fluid. Bradycardia is stopped with Atropine.
Alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists in case of an overdose of Moxonidine can reduce the manifestations of transient arterial hypertension. An imidazoline antagonist is administered as a specific antidote.
Moxonidine is a centrally acting antihypertensive drug and can lead to a decrease in heart rate, as well as relaxation of the smooth muscles of the walls. blood vessels. Has a similar mechanism of action antihypertensive drug from the group of ß-blockers Bisoprolol.
 It is worth understanding that not only the clinical effects of these drugs are almost identical, but also the side reactions of the body. That is why combining these drugs is categorically not recommended, as this can lead to increased negative symptoms, up to the development of signs of overdose.
It is worth understanding that not only the clinical effects of these drugs are almost identical, but also the side reactions of the body. That is why combining these drugs is categorically not recommended, as this can lead to increased negative symptoms, up to the development of signs of overdose.
Moxonidine for joint reception with antihypertensive agents of other groups leads to an additive effect. Also, the medicinal product is not prescribed with:
Taking this medication together with alcohol is strictly contraindicated. In some cases, the patient's blood pressure may rise sharply after drinking alcohol. In this condition, the blood vessels in the brain dilate, which can trigger an attack of hypertension and even a stroke.
If a patient encounters a similar phenomenon, then he needs to give up alcohol and not drink it even in minimal quantities.
When hypertensive crisis happened due to a hangover, then it is first necessary to detoxify the body in inpatient conditions or outpatient, but under supervision medical worker. In this case, it is necessary to periodically monitor the pressure level.
Taking alcohol simultaneously with Moxonidine increases the depression of the central nervous system, further dilates blood vessels and contributes to an increase in already high blood pressure.
This issue worries many patients, since the situation often arises that during long-term use of the drug, the pressure normalizes, but the course of therapy is still ongoing. It is known that Moxonidine is guaranteed to lower blood pressure and relieve patients from headache attacks.
But few people know that the big advantage of this medication is that it will not lower blood pressure below normal, which means the risk of stroke is eliminated.
This is due to the fact that Moxonidine not only reduces increased performance Blood pressure, but also normalizes metabolic processes in the myocardium.Moxonidine has several analogues, both Russian and foreign. The doctor will recommend which one to choose. Prices Russian drugs slightly lower, but the effect is approximately the same.

Foreign analogues include:

Whatever analogue the patient chooses, he must inform the attending physician about it. It is not recommended to select analogues on your own.
Treatment of arterial hypertension often requires the use of non-standard approaches - not the usual drugs, such as Bisoprolol or Enalapril, are prescribed, but second-line drugs, which are an alternative option.
Typical representatives of the pharmacological group are Moxonidine, analogues of Russian and foreign drugs that can only be recommended by the attending physician.
Tablets Moxonidine 0.2 mg
Treatment of arterial hypertension always begins with the prescription of a first-line drug (these include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, sartans and slow calcium channel blockers), however, if it is ineffective, as well as in the absence of a positive result from using a combination of drugs in this category , a second-line agent is prescribed.
A typical representative of the pharmacological group under consideration is Moxonidine, a drug that has an effect on the brain, due to which the clinical effect is realized.
It is necessary to note the high effectiveness of this drug, which is combined with the presence of a large number of undesirable side effects (it is this feature that is the reason that the entire pharmacological group is considered reserve drugs).
Taking it quite sharply reduces blood pressure levels - on average, blood pressure values drop by 30-40 divisions within half an hour, so after taking the drug, doctors recommend not getting out of bed for about 40-60 minutes, no less, in order to avoid dizziness and fainting.
In terms of its action, this drug has much in common with clonidine, but does not have such a strong hypnotic effect.
The active substance is moxonidine, and all other names that can be heard are nothing more than trade names for Moxonidine of the same drug (for example, Moxarel)
The mechanism of action of the drug Moxonidine is as follows:
Moxonidine and its analogs are contraindicated in the following cases:
The drug Moxonidine is available in the form of tablets of 0.200 mg.
The initial dosage of the drug is 0.200 mg per day, it is recommended to prescribe therapy with a single dose.
No addiction to this drug was observed, however, in the event of progression of arterial hypertension (and it still occurs sooner or later), it is recommended to increase the daily dose of the drug rather than adding drugs from another pharmacological group. This is the main difference in the principles of treating patients with first- and second-line drugs.
Please note that Moxonidine can be taken three times, but the daily dose should in no case exceed 0.600 mg. If necessary, the tablets can be divided in half; this will not affect the effectiveness of treatment in any way. When combining Moxonidine with any drug from the pharmacological group of beta-blockers, the principle of gradually replacing one drug with another should be observed.
Bisoprolol tablets 2.5 mg
For example, if treatment began with 0.200 mg Moxonidine and 5 mg Bisoprolol, then after a week it will be necessary to switch to 0.100 mg Moxonidine and 10 mg Bisoprolol, and after another week use only Bisoprolol alone (if 10 mg is enough to achieve a clinical effect, then not should increase the dose).
To be fair, it should be noted that such a need arises extremely rarely; usually, if a clinical effect is achieved by using Moxonidine, then it is not replaced with anything.
Often, patients take ACE inhibitors not so much to lower blood pressure, but to protect the kidneys from the harmful effects of vascular hypertension, so taking them together with centrally acting drugs is quite justified.
If the drug Moxonidine should be taken in the morning, then the ACE inhibitor should be consumed somewhere after 6-8 hours. It is this period of time that best contributes to the harmonious potentiation of the effects of drugs.
But it is much more difficult to combine Moxonidine with inhibitors of slow calcium channels (this need arises if the former are used as an antiarrhythmic). As a rule, Verapamil or Diltiazem is used. Here it will be necessary to titrate the dose of each drug - this is the task only of the attending cardiologist.
When canceling Moxonidine, you should also be guided by the same rule - only gradual withdrawal will avoid the occurrence of many unwanted side effects, so you should stick to the same scheme - 0.400 mg - 0.200 mg - 0.100 mg and only then cancel.
We are not talking about analogues, but about Moxonidine, produced by various manufacturers operating in the Russian Federation:
In fact, if drugs for lowering blood pressure that belong to the first line can be replaced and varied, selecting the most successful combination, then with centrally acting antihypertensive drugs everything is somewhat different - replacing one with another can only be done as a last resort, and then, such a scenario would be extremely undesirable.
The main reason is that a certain sensitivity is developed to all centrally acting drugs, as a result of which the withdrawal syndrome will be extremely pronounced.
In this case, we have to talk not about drug analogues in the literal sense of the term, but about generics:
So, if there is no domestic drug on pharmacy shelves, there is plenty to choose from.
To be fair, it should be noted that domestically produced analogues of Moxonidine are in no way inferior in quality to foreign ones - moreover, they have all received GMP certificates, which once again confirms the compliance of products of Russian companies with international quality standards.
Description and instructions for use of the drug Moxonidine in the video:
You may come across the statement that Clonidine is an analogue of Moxonidine, and one drug, if necessary, can be easily replaced with another. But in fact, this is absolutely not the case - they have no similarities, except that both drugs belong to the same pharmacological group. Even the recommended dosages differ, not to mention the contraindications and side effects.
moxonidine.
polyvinylpyrrolidone, Tween-80, magnesium stearate.
Release form
pharmachologic effect
Antihypertensive effect.
Active substance moxonidine is selective agonist HELL pressor influence
blood plasma blood-brain barrier metabolites.
Indications for use
The drug is prescribed for arterial hypertension in the anamnesis.
Contraindications
Side effects
Overdose
Accompanied headaches And dizzy, sedative effect, vomiting decrease in blood pressure gastric lavage, introductions activated carbon and laxative.
saline solution, bradycardia is stopped Atropine.
Specific antidote Idazoxan- well known imidazoline antagonist.
Interaction
Terms of sale
On prescription.
Storage conditions
Best before date
Up to three years.
special instructions
HELL, Heart rate And ECG
β-blocker
Analogues of Moxonidine
Reviews about Moxonidine
Reviews about the drug are positive, they confirm its effectiveness in lowering blood pressure, both with quick relief and with long-term treatment.
Moxonidine price, where to buy
The price of Moxonidine for a package of 0.2 mg 14 TB p/pl.o is approximately 120 rubles.
Moxonidine 0.2 mg 28 TB p/pl.o – 192-200 rubles.
Moxonidine 0.4 mg 14 TB p/pl.o – 165-180 rubles.
Moxonidine 0.4 mg 28 TB p/pl.o – 298 – 328 rubles.
Moxonidine-C3 tablets 0.2 mg 28 pcs. North Star JSC
Moxonidine-C3 tablets 0.4 mg 28 pcs. North Star JSC
Moxonidine Canon tablets 0.2 mg 28 pcs. Kanonpharma production CJSC
Moxonidine-C3 tablets 400 mcg 14 pcs. North Star JSC
Moxonidine Canon tablets 0.4 mg 14 pcs. Kanonpharma production CJSC
Moxonidine-SZ (tab.p.pl/vol.0.4 mg No. 60)
Moxonidine-SZ tablets 0.2 mg No. 28
Moxonidine (tab.p/pl/vol. 0.2 mg No. 20)
Moxonidine tablets 0.2 mg No. 14
Moxonidine-Canon tablets 0.2 mg No. 28
Moxonidine-SZNorthern Star ZAO, Russia
Moxonidine-SZNorthern Star ZAO, Russia
Moxonidine-SZNorthern Star ZAO, Russia
Moxonidine-SZNorthern Star ZAO, Russia
show more
Moxonidine 0.4 mg No. 30 tablet p.p.o. Lekfarm LLC (Belarus)
Moxonidine-Teva 0.4 mg No. 30 tablet p.p.o. Merckle GmbH (Germany)
Moxonidine-Teva 0.2 mg No. 30 tablet p.p.o. Merckle GmbH (Germany)
Moxonidine 0.2 mg No. 30 tablet p.p.o. Lekfarm LLC (Belarus)
show more
NOTE! Information about medications on the site is for reference and general information, collected from publicly available sources and cannot serve as a basis for making a decision on the use of medications in the course of treatment. Before using the drug Moxonidine, be sure to consult with your doctor.
Moxonidine*
I1.imidazoline receptor agonists
01.021 (Selective agonist of imidazoline receptors. Antihypertensive drug)
Antihypertensive agent. The mechanism of action of moxonidine is associated mainly with its effect on the central links of blood pressure regulation. Moxonidine is an agonist predominantly of I1-imidazoline receptors (to a much lesser extent - α2-adrenergic receptors). By stimulating these receptors of solitary tract neurons, moxonidine, through a system of inhibitory interneurons, helps to inhibit the activity of the vasomotor center and thus reduce descending sympathetic influences on the cardiovascular system. Blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) decreases gradually. The effect of moxonidine on the central nervous system is a sedative effect, which is, however, much less pronounced than that of clonidine, methyldopa and other centrally acting drugs. In addition, moxonidine causes dry mouth to a much lesser extent than these drugs.
After oral administration, it is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract - more than 90%. It is not subject to the “first pass” effect through the liver. Food intake does not affect the pharmacokinetics of moxonidine.
Plasma protein binding is 7%.
The main metabolites of moxonidine are 4,5-dehydromoxonidine and guanidine derivatives.
T1/2 is 2-3 hours.
Within 24 hours, more than 90% of moxonidine is excreted by the kidneys, approximately 70% unchanged.
Installed individually. The initial dose is on average 200 mcg orally 1 time / day, if necessary, the dose is increased to 400 mcg / day (less often - up to 600 mcg / day) in 1 or 2 doses.
When used simultaneously with beta-blockers, the effect of moxonidine on blood pressure increases. After discontinuation of moxonidine while continuing therapy with a beta-blocker, there is a risk of developing severe arterial hypertension (it is recommended to first discontinue the beta-blocker, and after a few days, moxonidine).
Drugs that have a depressant effect on the central nervous system (tranquilizers, hypnotics), ethanol enhance the depressive effect on the central nervous system.
When used simultaneously with antihypertensive drugs, the hypotensive effect is mutually enhanced.
Adequate and strictly controlled studies of the safety of moxonidine during pregnancy have not been conducted, so it should not be used in this category of patients.
It should not be used during lactation, since moxonidine is excreted in breast milk.
In experimental studies in animals, no negative effect of moxonidine on fertility was observed, no embryotoxic or teratogenic effects were detected, and no effect on perinatal and postnatal development was observed.
From the side of the central nervous system: at the beginning of treatment - headache, drowsiness, weakness, dizziness, sleep disturbances.
From the digestive system: at the beginning of treatment - dry mouth.
Arterial hypertension.
Severe bradycardia (less than 50 beats/min), SSSU, sinoatrial or AV block of the II and III degrees, severe arrhythmias, chronic heart failure of functional class IV according to the NYHA classification, unstable angina, severe renal and liver dysfunction, indications in the anamnesis of angioedema, increased sensitivity to moxonidine.
Due to the lack of clinical experience, moxonidine should not be used in patients with Raynaud's disease, intermittent claudication, epilepsy, parkinsonism, depression, or glaucoma.
Moxonidine is used with caution in patients with impaired renal function; in such cases, adjustment of the dosage regimen is required taking into account CC values.
During treatment with moxonidine, systematic monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, ECG is necessary, and in patients with impaired renal function, careful monitoring of their condition.
Due to the lack of clinical experience, moxonidine should not be used in children and adolescents under 16 years of age.
During the treatment period, caution should be exercised if it is necessary to engage in potentially hazardous activities that require concentration and high speed of psychomotor reactions.
TENZOTRAN tab, coated. film coating, 400 mcg: 14 or 28 pcs.
MOXONIDINE HEXAL tab, coated. coated, 200 mcg: 14, 28 or 30 pcs.
MOXONIDINE tab, coated. coated, 200 mcg: 14 or 20 pcs.
MOXOGAMMA® (MOXOGAMMA) tab, coated. film coating, 400 mcg: 30 pcs.
MOXONITEX tab., coated. film-coated, 300 mcg: 7, 10, 14, 20, 21, 28, 30, 35, 40, 42, 50, 56 or 70 pcs.
MOXONITEX tab., coated. film-coated, 400 mcg: 14 pcs.
TENZOTRAN tab, coated. film coating, 200 mcg: 14 or 28 pcs.
TENZOTRAN tab, coated. film shell, 300 mcg: 14, 28 or 42 pcs.
PHYSIOTENS® tab, coated. film coating, 400 mcg: 14, 28 or 98 pcs.
MOXONITEX tab., coated. film-coated, 200 mcg: 14 pcs.
MOXONIDINE HEXAL tab, coated. coated, 400 mcg: 14, 28 or 30 pcs.
PHYSIOTENS® tab, coated. film coating, 200 mcg: 14, 28 or 98 pcs.
CYNT® tab, coated. coated, 300 mcg: 10, 14, 20, 28, 30, 40, 42 or 56 pcs.
CYNT® tab, coated. coated, 400 mcg: 10, 14, 20, 28, 30, 40, 42 or 56 pcs.
MOXONIDINE HEXAL tab, coated. coated, 300 mcg: 14, 28 or 30 pcs.
MOXOGAMMA® (MOXOGAMMA) tab, coated. film coating, 300 mcg: 30 pcs.
PHYSIOTENS® tab, coated. film coating, 300 mcg: 14, 28 or 98 pcs.
MOXOGAMMA® (MOXOGAMMA) tab, coated. film coating, 200 mcg: 30 pcs.
CYNT® tab, coated. coated, 200 mcg: 10, 14, 20, 28, 30, 40, 42 or 56 pcs.
Table of analogues and prices
Physiotens (original Moxonidine) - official instructions for use (abstract)
All about blood pressure monitors
There are contraindications. Before starting use, consult your doctor.
Commercial names abroad (abroad) - Gilutens, Moxaviv, Moxocard, Moxodura, Moxon, Normatens, Ratiomox.
Other centrally acting antihypertensive drugs are here.
All drugs used in cardiology are here.
You can ask a question or leave a review about the medicine (please, do not forget to indicate the name of the drug in the text of the message) here.
Preparations containing Moxonidine (ATC code C02AC05):
| Name | Release form | Packaging, pcs. | Manufacturer country | Price in Moscow, r | Offers in Moscow |
| tablets 0.2 mg | 14 | Germany, Rottendorf | 180- (average 272↗) -468 | 723↗ | |
| Physiotens - original | tablets 0.4 mg | 14 | Germany, Rottendorf | 368- (average 436) -496 | 581↗ |
| Moxonitex | tablets 0.4 mg | 14 | Germany, Salutas | 242- (average 320↘) -426 | 111↘ |
| Tenzotran | tablets 0.2 mg | 14 | Israel, Perrigo | for 14 pieces: 143- (average 177) -205; for 28pcs: 228- (average 332) - 389 |
452↗ |
| Tenzotran | tablets 0.4 mg | 14 | Israel, Perrigo | for 14 pieces: 183- (average 306↘) -598; for 28pcs: 491- (average 564) - 636 |
323↗ |
| Moxonidine | tablets 0.2 mg | 14 and 28 | Russia, Pharmzaschita | 89- (average 203↗) -255 | 226↗ |
| Moxonitex | tablets 0.2 mg | 14 | Germany, Salutas | 150- (average 166) -189 | 11 |
| Moxogamma | tablets 0.3 mg | 30 | Germany, Artesan | No | No |
| Cynt | tablets 0.2 mg | Germany, Eli Lilly | 100 | No | No |
| Cynt | tablets 0.3 mg | Germany, Eli Lilly | 30 | No | No |
| Cynt | tablets 0.4 mg | Germany, Eli Lilly | 100 | No | No |
Which generic is better?
Where can I buy?
Selective agonist of imidazoline receptors. Antihypertensive drug
Centrally acting antihypertensive drug.
Moxonidine is an antihypertensive drug with a central mechanism of action. In the brain stem structures (rostral layer of the lateral ventricles), moxonidine selectively stimulates imidazoline-sensitive receptors that take part in the tonic and reflex regulation of the sympathetic nervous system. Stimulation of imidazoline receptors reduces peripheral sympathetic activity and blood pressure.
Moxonidine differs from other sympatholytic antihypertensive drugs in its lower affinity for α2-adrenergic receptors, which explains the lower likelihood of developing sedation and dry mouth.
Taking moxonidine leads to a decrease in systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure. The hypotensive effect of moxonidine has been confirmed in double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized studies.
Physiotens® increased the insulin sensitivity index by 21% (compared to placebo) in patients with obesity, insulin resistance and moderate arterial hypertension.
Suction
After oral administration, moxonidine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the upper gastrointestinal tract. Absolute bioavailability is approximately 88%. The time to reach Cmax is about 1 hour. Food intake does not affect the pharmacokinetics of the drug.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding is 7.2%.
Vd - 1.4-3 l/kg. Penetrates through the BBB.
Metabolism
The main metabolite of moxonidine is dehydrogenated moxonidine and guanidine derivatives. The pharmacodynamic activity of dehydrogenated moxonidine is about 10% compared to moxonidine.
Removal
T1/2 of moxonidine and metabolite is 2.5 and 5 hours, respectively. Within 24 hours, more than 90% of moxonidine is excreted by the kidneys (about 78% unchanged and 13% as dehydriromoxonidine, other metabolites in the urine do not exceed 8% of the dose taken). Less than 1% of the dose is excreted through the intestines.
Compared with healthy volunteers, patients with arterial hypertension show no changes in the pharmacokinetics of moxonidine.
Clinically insignificant changes in the pharmacokinetic parameters of moxonidine were noted in elderly patients, probably due to a decrease in the intensity of its metabolism and/or slightly higher bioavailability.
Moxonidine excretion is significantly correlated with CC. In patients with moderate renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min), steady-state plasma concentrations and final T1/2 are approximately 2 and 1.5 times higher than in individuals with normal renal function (creatinine clearance more than 90 ml/min). In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), steady-state plasma concentrations and final T1/2 are 3 times higher than in patients with normal renal function. The administration of multiple doses of moxonidine leads to predictable accumulation in the body of patients with moderate and severe renal failure. In patients with end-stage renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min) on hemodialysis, steady-state plasma concentrations and final T1/2 are 6 and 4 times higher, respectively, than in patients with normal renal function. In all groups, the maximum concentration of moxonidine in blood plasma was 1.5-2 times higher. In patients with impaired renal function, the dosage should be adjusted individually. Moxonidine is excreted to a small extent during hemodialysis.
The tablets are taken orally, regardless of meals.
In most cases, Physiotens® is prescribed at an initial dose of 200 mcg per day. The maximum single dose is 400 mcg; the maximum daily dose is 600 mcg (divided into 2 doses).
For patients with moderate or severe renal failure and patients on hemodialysis, the daily dose is 200 mcg. If necessary and well tolerated, the daily dose can be increased to 400 mcg.
From the side of the central nervous system: often (1-10%) - headache, dizziness, drowsiness; infrequently (< 1%) - бессонница.
From the cardiovascular system: rarely (< 0.1%) - чрезмерное снижение АД, ортостатическая гипотензия.
From the digestive system: often (1-10%) - dry mouth; infrequently (< 1%) - тошнота.
Dermatological reactions: uncommon (< 1%) - кожная сыпь, зуд; очень редко (< 0.01%) - ангионевротический отек.
General reactions: often (1-10%) - asthenia.
Most common: dry mouth, headache, dizziness, asthenia and drowsiness. These symptoms often improve after the first weeks of therapy.
The drug should be prescribed with caution in severe renal failure and in terminal stage; patients on hemodialysis; severe liver failure more than 9 points on the Child-Pugh scale ( clinical experience application is insufficient).
There are no clinical data on the treatment of pregnant women with moxonidine. Physiotens® should be prescribed with caution during pregnancy, only after a careful assessment of the risk-benefit ratio, when the benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Moxonidine is excreted in breast milk. If it is necessary to use the drug during lactation, breastfeeding is recommended to stop or discontinue the drug.
In experimental studies on animals, direct or indirect Negative influence pregnancy, embryonic/embryonic development, childbirth or postnatal development have not been established.
Use with caution in cases of severe liver failure (clinical experience is limited)
For patients with renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min) and patients on hemodialysis, the initial single dose is 200 mcg. The maximum daily dose is 400 mcg.
Use with caution in severe chronic renal failure
If it is necessary to cancel simultaneously taken beta-blockers and the drug Physiotens®, first cancel the beta-blockers and only after a few days - Physiotens®.
During treatment with Physiotens®, regular monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate and ECG is necessary.
You should stop taking Physiotens® gradually.
There is no data on the adverse effects of moxonidine on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machines and mechanisms. There are reports of drowsiness and dizziness during treatment with moxonidine, which should be taken into account in patients engaged in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
There have been reports of several cases of non-fatal overdose when doses up to 19.6 mg were used simultaneously.
Symptoms: headache, sedation, drowsiness, marked decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, fatigue, asthenia, bradycardia, dry mouth, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region. A short-term increase in blood pressure, tachycardia, and hyperglycemia are also potentially possible.
Treatment: There are no specific antidotes. In case of arterial hypotension, it is recommended to restore bcc through the administration of fluid and dopamine.
Bradycardia can be relieved with atropine.
α-Adrenergic antagonists may reduce or eliminate the paradoxical hypotensive effects of moxonidine overdose.
When using the drug Physiotens® simultaneously with other antihypertensive drugs (including thiazide diuretics, blockers of “slow” calcium channels), an additive effect is observed.
Tricyclic antidepressants may reduce the effectiveness of centrally acting antihypertensive drugs, so their use together with Physiotens® is not recommended.
Physiotens® is able to moderately improve impaired cognitive function in patients receiving lorazepam.
Prescribing Physiotens® together with benzodiazepines may be accompanied by an increase in the sedative effect of the latter.
When Physiotens is prescribed together with moclobemide, there is no pharmacodynamic interaction.
When prescribing Physiotens with hydrochlorothiazide, glibenclamide or digoxin, no pharmacokinetic interaction was detected.
The drug is available with a prescription.
List B. The drug should be stored out of the reach of children.
The drug in the form of 200 mcg tablets should be stored at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Shelf life - 2 years.
The drug in the form of tablets 300 mcg and 400 mcg should be stored at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Shelf life - 3 years.
The instructions are quoted from the Vidal reference book.
Return to top of page
Be careful, the drug is prescribed to women during pregnancy, when there is no negative effect on the condition of the mother and her child. Buyers pay 270-780 rubles for a medical product.
In addition to the original medicine, cheap analogues of the drug are produced.
The composition of the ingredient, similar to Russian production, contains the main active substance.
| Name | Price in rubles | About the drug |
| Moxarel | from 13-350 | Inexpensive and effective drug. After using the medication, systolic pressure decreases; the composition of the drug interferes with the action of the vasomotor center. The product of a domestic manufacturer actively affects a well-known disease - arterial hypertension |
| Moxonidine | from 115-220 | Inexpensive and effective medicine. High blood pressure is treated with similar imported drugs. Children and adolescents under 16 years of age should not take the medicine |
| Moxonidine Canon | from 145-240 | Inexpensive and effective drug. A similar medicine containing a similar active drug. |
The group of pharmacological medicines includes similar medicines produced in Ukraine. The products are inexpensive compared to the originals.
The list contains synonyms of the original product, they are not considered substitutes similar to the original ingredient.
Similar medicines contain similar indications for use as the original product.
The product is sold at an average price of 15-120 rubles. By type, clonidine is produced in two forms:
Clonidine hydrochloride is one of the main active substances. Modern medications are antihypertensive, arterial hypertension is the area of application. In addition to these diseases, the product treats high blood pressure.
The cheapest analogue is purchased at a price of 45-55 rubles. The tablets have a pronounced hypotensive effect.
The drug is intended to increase renal blood circulation, it has a strong antiarrhythmic effect.
Thanks to the effectiveness of the drug Ruanatine, you can calm frayed nerves. Cheap Ukrainian-made products are used to treat mild and moderate arterial hypertension.
The medicine is available at pharmacy kiosks at an average cost of 40-65 rubles. The drug is intended to lower high blood pressure and is purchased at a low cost.
The active ingredient of the drug is maleate. It has the following indications for use: treats arterial hypertension, which requires complex therapy.
Inexpensive Belarusian generics containing the active element moxonidine are suitable as a replacement for a cheap product.
Medicines made in Belarus, which are similar in composition and action to tablets, are found in small quantities. The table below consists of one title.
Below is a list of imported medications that can be replaced with an inexpensive antihypertensive drug.
The medicine is sold at an average price of 180-600 rubles. The main ingredient is the constituent substance of the medicine. Arterial hypertension is treated with medication.
Tablets made in Germany. Products are sold at an average price of 185-59 rubles.
The ingredient is intended for the treatment of acute diseases:
Has no negative effect on cardiac output, and also does not affect the normal heart rate.
A medicinal product is used to eliminate a disease such as arterial hypertension, with varying degrees of complexity.
The analogue is sold in pharmacy kiosks, with average prices ranging from 300-380 rubles. The product belongs to the group of antiadrenergic drugs, the synonyms of the analogue have a central effect. Prescribed to patients with arterial hypertension.
Symptoms such as dizziness, drowsiness, as well as dry mouth, are considered common adverse events.
The severity of side effects decreases sharply if you are treated with tablets for a long time. According to a doctor's prescription, patients buy products at a pharmacy kiosk.
© 2017 Women's magazine | Womans7 · Copying site materials without permission is prohibited
When a person of any age suffers from hypertension, the drug Physiotens, analogues of which are also produced in our country, will help alleviate the condition and return to an active life.
Hypertension is a common disease characterized by increased blood pressure. People suffering from this disease are very sensitive to change. weather conditions. According to WHO, every second person on the planet periodically suffers from headaches caused by high blood pressure (BP). So far, doctors believe that people who are most susceptible to such a disease are those who suffer from excess weight, diseases of the cardiovascular system, or have genetic abnormalities, peculiarities. According to statistics, older people suffer from this disorder 10 times more often than young people.
To localize the manifestations of arterial hypertension, the patient has to take medications on a regular basis, and not just during exacerbations. And this despite the fact that every medicine has side effects that, although in small quantities, still affect the body. One of the best drugs prescribed for hypertension in the post-Soviet space is the German drug Physiotens. It is based on a substance such as moxonidine (helps to normalize the work nervous regulation, dilates blood vessels). This drug is suitable for those who:
One of the main advantages that Physiotens has is that it does not require strict adherence to the dosage schedule. That is, the patient can take the medicine whenever he wants, without reference to food intake. Most often, this drug is used in combination with other medications (does not affect the effectiveness of third-party medications).
Physiotens stimulates the work of the heart, and due to this, special receptors are produced in the brain stem that are responsible for the reflex and tonic regulation of the nervous system. In addition, the substances produced reduce sympathetic activity, which affects the functioning of the heart and normalizes blood pressure. Physiotens is characterized by the absence of interaction with adrenergic receptors. This feature allows patients taking this medicine to forget about the sedative effect and dry mouth.
In patients after taking this medication, metabolism is normalized (quantitative indicators of triglycerides, cholesterol, blood glucose), and a decrease in vascular resistance is observed. The effectiveness of the drug has been repeatedly confirmed by clinical studies (several hundred of them were conducted). Even in insulin-dependent people and those who suffer from obesity, taking the drug lowered blood pressure; In addition, it is quickly eliminated from the body and is compatible with other drugs. The medicine is applicable as a constant in the composition complex therapy, and once (on an empty stomach, before and after meals).
Since Physiotens is primarily a centrally acting drug, it is not recommended for people who are underweight or have a fast metabolism. In addition, the drug is contraindicated in people who are hypersensitive to moxonidine and galactose.
In such patients, the medicine can cause fever, stomach upset, and severe itching. Physiotens is not recommended for women during lactation (there is a possibility that active medicinal substances from the drug can enter the child’s body through milk).
The components of Physiotens affect the kidneys and heart, so it should be taken only after the recommendation of an experienced doctor and under his strict supervision. Despite the safety of the drug, in some patients it may cause:
Some patients taking the drug experienced fainting and heart problems.
It is financially difficult for hypertensive patients, especially the elderly, to constantly buy Physiotens - domestically produced analogues are much cheaper, and some are even safer.
Usually, pharmacists and pharmacists select a drug from pharmacies based on the active ingredient - for Physiotens it is Moxonidine. However, you should not rely entirely on the pharmacy worker. It is better to listen to your doctor, especially since analogues may have completely different purification from excipients during production or be supplemented with specific components that are contraindicated for the patient.
Most Popular Russian analogue European Physiotens - Moxarel. It is also a selective imidazoline receptor agonist. Its cost is lower than the German drug, but it has a similar composition. The second popular medicine is an analogue of Physiotenza, the drug Moxonidine Canon, which received the same active ingredient (moxonidine) in a dosage of 0.2-0.4 mg. This selective imidazoline receptor agonist regulates the sympathetic nervous system tonically and reflexively.
On the Russian pharmaceutical market, Moxonidine is found more often than foreign analogues due to High Quality production and prices affordable for the population. Its composition, like that of foreign taxes, has an effective effect on the patient’s body (pressure is normalized without dry mouth or sedation). The medicine initially relieves the person taking it from discomfort, and it begins to act within 1 hour after administration. For this efficiency, many people in the Russian Federation choose it. The daily dose of Moxonidine is the same as that of German tablets. It can be adjusted by the doctor depending on the individual characteristics of the patient. Due to the absence of an additive effect (no addiction to the drug), the tablets can be taken simultaneously with other medications.
This drug is not recommended for pregnant and lactating women due to the lack of clinical studies of use during pregnancy and lactation. You should not experiment with taking this medicine on your own - you may experience various kinds complications. Like foreign analogue, shelf life is 24 months.
Many Russian medicines have long shown their effectiveness; they are not inferior to foreign ones, and Moxonidine is direct proof of this. It corresponds in all respects German drug Physiotens or Swiss Tenzotran. One tablet of this medicine contains 200 or 400 mcg of moxonidine and 64 mg of lactose monohydrate. In addition, there is microcrystalline cellulose (29.8 mg), 2 mg of povidone K30 and croscarmellose sodium, 1 mg of magnesium stearate and colloidal silicon dioxide.
The drug is supplied in packs of 30 or 14 tablets. The tablets themselves yellow color with a biconvex, round shape with a shell. Indications: to take for arterial hypertension, metabolic syndrome.
This drug is prohibited for patients with:
Can be taken regardless of food intake.
It is important to remember that Moxarel, like its substitutes, should not be taken with an increase in the daily dose, which should not exceed 600 mg. Even in severe cases it should be divided into 2 doses. For most patients using the medicine, 200 mcg/day is enough.
If the patient suffers from moderate or even severe renal failure or is on hemodialysis, then the initial dose should not exceed 200 mcg/day. Only in case of good tolerance and urgent need is it possible to increase the daily dose to 400 mcg.
It is not advisable to use the substance in persons who have been diagnosed with serious illnesses coronary vessels, unstable angina, heart failure.
An overdose of Moxarel is accompanied by the following symptoms:
If these symptoms are detected, the patient should notify his or her physician.
When taking a domestic drug, it is important to remember that it can enhance the effects of other drugs on the body, for example, sleeping pills, sedatives, tranquilizers or tricyclic antidepressants. Moxonidine may moderately improve impaired cognitive function in people taking Lorazepam. If you use Moxonidine together with drugs based on benzodiazepine derivatives, you can get a strong sedative effect.
The use of the drug in conjunction with beta-blockers in a patient will cause increased bradycardia. It has not been clinically confirmed that abrupt discontinuation of the drug Moxarel leads to an increase in blood pressure. But doctors recommend stopping use gradually, gradually reducing the dose over 14 days. It is advisable to carry out treatment with Moxarel with regular monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure; in addition, ECG checks are necessary.
Important: during the entire course of treatment it is prohibited to drink alcohol-containing drinks.
Since it has not been clinically established what specific effect it has on pregnant women, drugs from this group should be used carefully, with a careful assessment of possible risks.
It is important to remember that Moxonidine is easily transmitted to a child through breast milk. Doctors strongly recommend that you stop breastfeeding for the period of treatment. If this is not possible, be sure to stop taking the medication.
Manufacturers prohibit the use of the medicine by minors. This is due to the lack of clinical studies. In addition, it is not recommended to use the drug for elderly people (over 75 years old).
To maximize the effectiveness of treatment, it is important to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and find out the root cause. Only after going through the entire range of examinations and consulting with a specialist should you begin treatment. Moxarel and similar drugs Not recommended for people with hypersensitivity to galactose and moxonidine.
Physiotens tablets have an analogue not only of domestic production. There are also European substitutes. So, there is a German Moxogamma, Swiss drug Moxonitex, Israeli Tenzotran. They differ in dosages and packaging (by the number of tablets), but have the same active ingredient. Depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, he can choose a medicine for himself, but only with the help of an experienced doctor and under his close supervision.
Any medicine has side effect, however, for similar drugs they can differ greatly. Based on the effect on the patient’s body, the doctor prescribes the most effective drug.
Anyone who is recommended Moxogamma should know that it is almost no different from Physiotens (it has the active ingredient moxonidine), however, the other components in the composition are addictive to the body. Therefore, you should not suddenly stop taking it. So, with long-term use, you need to wean off only gradually, otherwise negative consequences for the body are guaranteed.
One tablet contains 200 mcg of active ingredient moxonidine.
Microcrystalline cellulose, Klucel, Aerosil grade A-380, castor oil, polyvinylpyrrolidone, Tween-80, magnesium stearate.
The drug is produced in film-coated tablets, in cellular packaging of 14 pieces, in a cardboard pack there can be 14, 28 pieces - 1 or 2 blisters.
Antihypertensive effect.
Active substance moxonidine is selective agonist imidazoline receptors and is responsible for tonic and reflex control of the sympathetic nervous system, localized in the medulla oblongata in the venterolateral section. The drug is able to reduce systolic and diastolic HELL with a one-time dose and long-term therapy due to the reduction pressor influence sympathetic system on peripheral vascular resistance and peripheral vasculature, without significant changes in cardiac output and heart rate.
Absorption occurs 90% regardless of meals. Bioavailability is 88% and 7% is protein bound blood plasma. The substance can pass through blood-brain barrier, penetrate into milk, long-term use does not lead to accumulation. The maximum concentration in plasma is reached after 0.5-3 hours and is 1-3 picograms per ml, taking into account that the volume of distribution is in the range of 1.4-3 liters per kg. The half-life is several hours. 90% is excreted by the kidneys, with 70% unchanged, the rest in the form metabolites.
The drug is prescribed for arterial hypertension in the anamnesis.
Side effects
The drug Moxonidine can cause the following adverse reactions:
Moxonidine, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
Taken orally, starting with a dose of 200 mcg once a day. The maximum acceptable single dose should be no more than 400 mcg, while the acceptable daily dose should be up to 600 mcg in two doses. Instructions for use of Moxonidine indicate the need to adjust the daily dose on an individual basis based on data on the tolerability of therapy.
Overdose
Accompanied headaches And dizzy, sedative effect, vomiting, cramps in the stomach, excessive decrease in blood pressure with general weakness and dry mouth. Treatment is prescribed symptomatically in the form of gastric lavage, introductions activated carbon and laxative.
Reducing blood pressure requires restoring blood volume by administering saline solution, bradycardia is stopped Atropine.
Specific antidote Idazoxan- well known imidazoline antagonist.
Interaction
The combined use of the drug Moxonidine with the following drugs and drugs leads to:
Terms of sale
On prescription.
Storage conditions
In a dry, dark place, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Best before date
Up to three years.
special instructions
Treatment requires regular monitoring HELL, Heart rate And ECG, it is advisable to exclude drinking alcohol, working with machinery and driving a car, as well as other activities that require increased attention or high speed of reactions. It is necessary to stop the course gradually.
If cancellation is necessary at the same time β-blocker c and Moxonidine, then β-blockers must initially be discontinued, then after a few days Moxonidine can be discontinued.
Analogues of Moxonidine Level 4 ATX code matches:
Synonyms of this drug contain the same active substance, while analogs of Moxonidine (or in other words - generics) can only have a similar therapeutic effect, among them the most popular are: